Water Pump for Engine

How does a water pump for an engine work?
- How a Water Pump Works
- Different Types
- Choosing an Electric Water Pump
- Connections
- Installation of Electric Water Pump
- Accessories
- Problems
1 ▼
How a Water Pump Works
The water pump is the heart of the cooling system; it is a centrifugal pump that circulates coolant through the system to keep the engine at the correct temperature. A water pump is driven mechanically by a belt connected to the crankshaft or electrically, which we will discuss more about below.
The cooling system in an engine operates in a loop and always passes through the water pump. If the water pump is stationary, the water remains still. When the water pump spins, the water circulates as well. If the water were to remain still, it would boil at the points where it is hottest, which is typically around the cylinder walls where the pistons move. When the water pump starts and circulates the water, heat is transported away from these points, distributing the heat throughout the water and the engine block.
Coolant can only hold a certain temperature before it begins to boil; therefore, a radiator is needed. The water circulates only within the engine until the operating temperature is reached. This is controlled by a thermostat in a system with a mechanical water pump. When the water temperature reaches the thermostat's opening temperature (for example, 92 degrees Celsius), the thermostat opens, allowing the water to circulate through the radiator as well. The water circuit in the cooling system works the same way as before, but now the water circulates through the radiator as well. When the water cools down below 92 degrees, the thermostat closes again until the water reaches 92 degrees, at which point it opens again. This is how the cooling system works, simply explained.
If the car is stationary and the radiator cannot benefit from the airflow, the cooling fan mounted on the radiator is activated instead. This is activated with the help of a temperature sensor.
2 ▼
Different Types
Original Water PumpIs typically belt-driven and is recommended to be replaced during a timing belt change, as the pump contains a bearing that wears out over time. (100,000+ miles on an original car)
Electric Water Pump
Is an electrically controlled water pump powered by the car's electrical system from the car battery. It is important to distinguish between an electric water pump that is meant to drive the cooling system and a circulation pump, which is an additional component that is mounted on original cars to circulate the fluid when the car is turned off and requires additional cooling. This is controlled by the main pump in the aftermarket and in racing/motorsport.
Combination
An electric water pump can be used alongside the original mechanical pump, but can also operate completely independently without the mechanical water pump. See more information below.
3 ▼
Choosing an Electric Water Pump
When choosing an electric water pump, you ensure that it fits your build and that it has sufficient flow for your engine. A mechanical water pump, on the other hand, follows the engine RPM and provides circulation based on the RPM.
Low RPM = Less water flow
High RPM = More water flow
An electric water pump has a consistent flow all the time regardless of RPM. Off or on. However, the pump can also be controlled electronically through accessories such as the ECU or PWM modules. This way, the flow can be controlled freely and depending on the control unit, can even be optimally "mapped" in.
Some guidelines when choosing a water pump:
- Engine displacement: 2.0L = ~80l/min
- Engine displacement: 2.0 - 3.5L = ~115l/min
- Engine displacement: 3.5 - 5.0L = ~130l/min
- Engine displacement 5.0L and more =~150l/min
If you have the option to PWM control your water pump, feel free to use a larger pump than you need, as you can always restrict the flow but can never exceed the pump's maximum capacity.
4 ▼
Connections
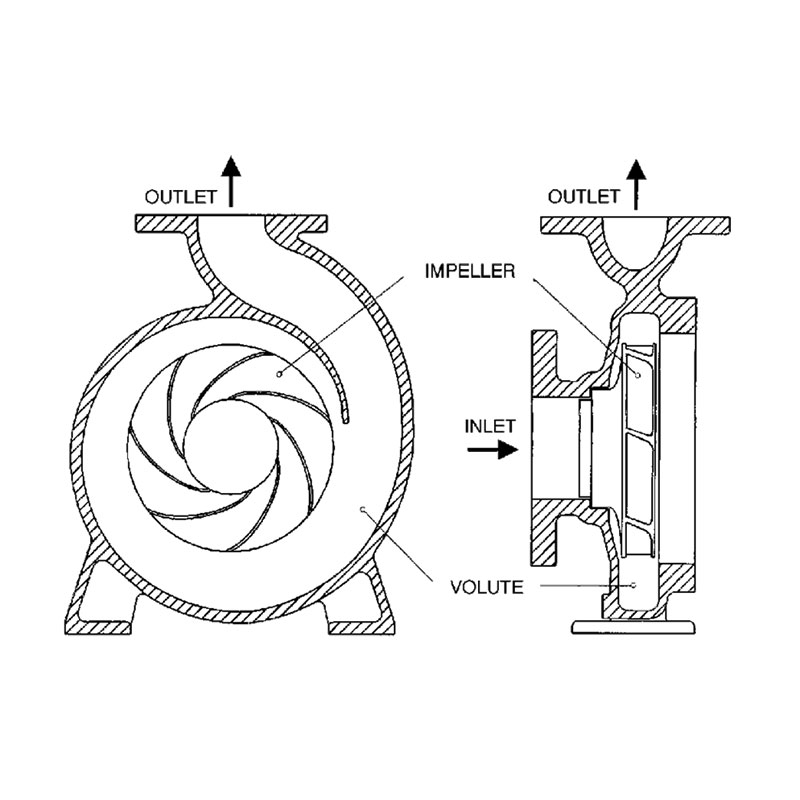
A water pump has two connections - An outlet and an inlet. These are typically hose connections, but internal threads may also be present. There is also an electrical connector and sometimes a mounting device if it does not need to be purchased as an accessory or manufactured.
Inlet
The inlet is at the center of the water pump. This is similar to all centrifugal pumps. The same applies to turbochargers, where the inlet is located in the center.
Outlet
The outlet is where the water is expelled from the pump. The outlet is located on the side of the pump, as it is on all centrifugal pumps. You can imagine that a centrifugal pump uses centrifugal force to fling the water out to the side. Hence, the outlet is positioned on the side.
Connector
The electrical connector has two poles. This is polarity-sensitive and is therefore marked with plus and minus. Note this carefully; otherwise, the water pump may rotate in reverse.
Mounting
Mountings can vary; they are usually model-specific to the pump, but in the aftermarket, it is common for these to be custom-made.
5 ▼
Installation of Electric Water Pump
A mechanical water pump is mounted as original equipment and has its designated place on the engine block. This is not something you change. However, if you are using an electric water pump, there are a few considerations to keep in mind when installing it.
You can choose between these different installations:
- Install as an additional water pump
- Install as the main pump (simple installation)
- Install as the main pump (good installation)
- Install as the main pump (optimal installation)
The water pump should be mounted on the lower radiator hose as one of the lowest parts of the cooling system.
This allows air to be evacuated from the pump - upwards.
- Let the mechanical water pump remain in place.
- Install the electric water pump on the lower radiator hose.
- The thermostat should remain in place, but drill two 3mm holes to allow for some circulation.
- Let the mechanical water pump remain in place.
- Install the electric water pump on the lower radiator hose.
- Remove the thermostat completely.
- Disconnect the belt drive from the original water pump by selecting a different, shorter drive belt.
Note! If you are going to operate this way, you must drill two 3mm holes in the thermostat to allow for some circulation before the thermostat opens, so that it doesn't cause localized boiling around the cylinders.
- Remove the OEM water pump and take out the impeller (the part that circulates the water).
- Reinstall the OEM water pump; now you can use the pulley on the water pump and the original drive belt without any effect on the water circulation.
- Install the electric water pump on the lower radiator hose.
- Remove the thermostat completely.
Note! Check that the OEM water pump does not have more than one inlet and outlet. If so, check how the water should be routed around the engine for optimal circulation.
- Remove the OEM water pump completely.
- Remove the thermostat completely.
- Use a different, shorter drive belt (water pump removed).
- Purchase / manufacture a replacement plate / adapter instead of the OEM water pump. A blanking plate or an adapter plate to which the water pump is mounted.
An electronic water pump is sensitive to air pockets. If an air pocket gets trapped in the pump, it will function very poorly or not at all. To eliminate air, the pump should be angled with the outlet facing upwards so that the air can rise/evacuate from the pump. Ideally, the pump should be mounted this way, but it is sufficient to do this as a bleeding procedure when the system is being filled with water.
NOTE! Do not run the water pump without water at startup!

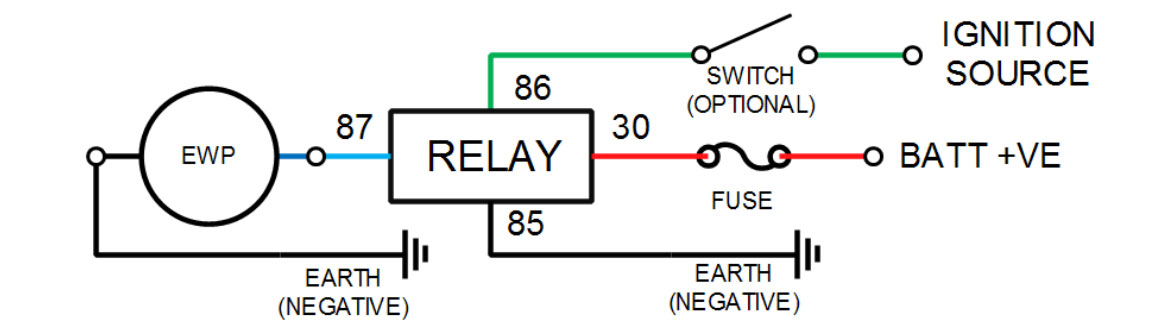
To connect the electric water pump without control / controller. Follow the image below. If a digital controller or ECU is used, then follow the accompanying instructions as they may vary by manufacturer.
(image from Davies Craig)
6 ▼
Accessories
- Water Pump Adapter for Engine Block
Adapters to fit aftermarket water pumps to various engine blocks.
Adapters for mounting external water pumps in original mounts. - Water Pump Controller
Digital water pump control to set the function of your cooling system. - Thermostat
The thermostat's role is to prevent coolant from entering the radiator unless cooling is needed. For example, during startup of a cold engine, you want to reach the engine's operating temperature as quickly as possible. Only once this has happened does the thermostat open and close to maintain an operating temperature typically around 82-92 degrees. - Gaskets:
Used primarily for sealing against the engine block to prevent leakage (applies to OEM pump). - Temperature Sensor
Used to provide the water pump controller and ECU with information about the current water temperature. - Wiring / Connectors
Used for a safe and tidy electrical installation of the water pump. - Drive Belt
To drive your mechanical water pump using the crankshaft. Also called a multi-rib belt.
7 ▼
Problems
If you have problems with your water pump, there is a risk that you will overheat the engine. Clear signs of a faulty water pump are unusual sounds such as rattling or whistling. Always make sure to measure the water temperature regardless of the type of pump you are using.
Water leakage from OEM water pump
If coolant leaks through the OEM water pump or steam comes from the water pump, it can indicate that it is faulty. It has a hole designed to notify when the pump has started to wear out and needs to be replaced.
Heating up quickly
If the engine heats up very quickly, this indicates poor circulation and there is a risk that the water will start to boil around the cylinders.
Strange noises at startup
Since electric water pumps often have small margins in a cast housing, the impeller may sometimes rub slightly against the housing. This creates a noise that is normal but should quiet down after a while.
▼
▼
-
Engine and tuning
- Crankcase ventilation Information
- Engine block: Parts and how they fit together
- Engine deck clearance
- Head gasket - Information
- Engine bearing installation
- Engine bearing Information
- Blow off valve: Information and assembly
- Electronic Throttle Housing - DBW Information
- Noise from engine - Troubleshooting
- ARP bolts: Material and specifications
- Assembly of connecting rods
- Automotive cooling system problem
- Engine cooling system [How does it work?]
- Engine Oil system
- Engine water pump
- Exhaust pipe: Which material should you choose? [+extra information]
- Exhaust system: Parts and assembly
- Exhaust values - Information
- Exhaust wrap
- Intercooler guide
- Oil cooler - Information and FAQ
- Piston ring installation TIPS
- What do notes on Wiseco & JE pistons mean?











































