Intercooler guide

What does an Intercooler do?
intercooler function in 3 steps:- An intercooler / charge air cooler cools the intake air in a supercharged engine.
- The air from the turbo to the engine is hot and should be cooled as colder air has a higher density and more oxygen.
- More oxygen in the engine mean higher efficiency / engine power.
1. Turbo
The engine's hot exhaust gases powers the turbo and allow supercharged fresh air to be forced into the engine. The fresh air is quickly heated by the hot turbo. Therefore, an intercooler is used to cool the intake air again.

2. Intercooler
An intercooler is used to cool the intake air in a supercharged engine. The air is cooled down because cold air has higher density and more oxygen than hot air and therefore gives a higher engine efficiency.

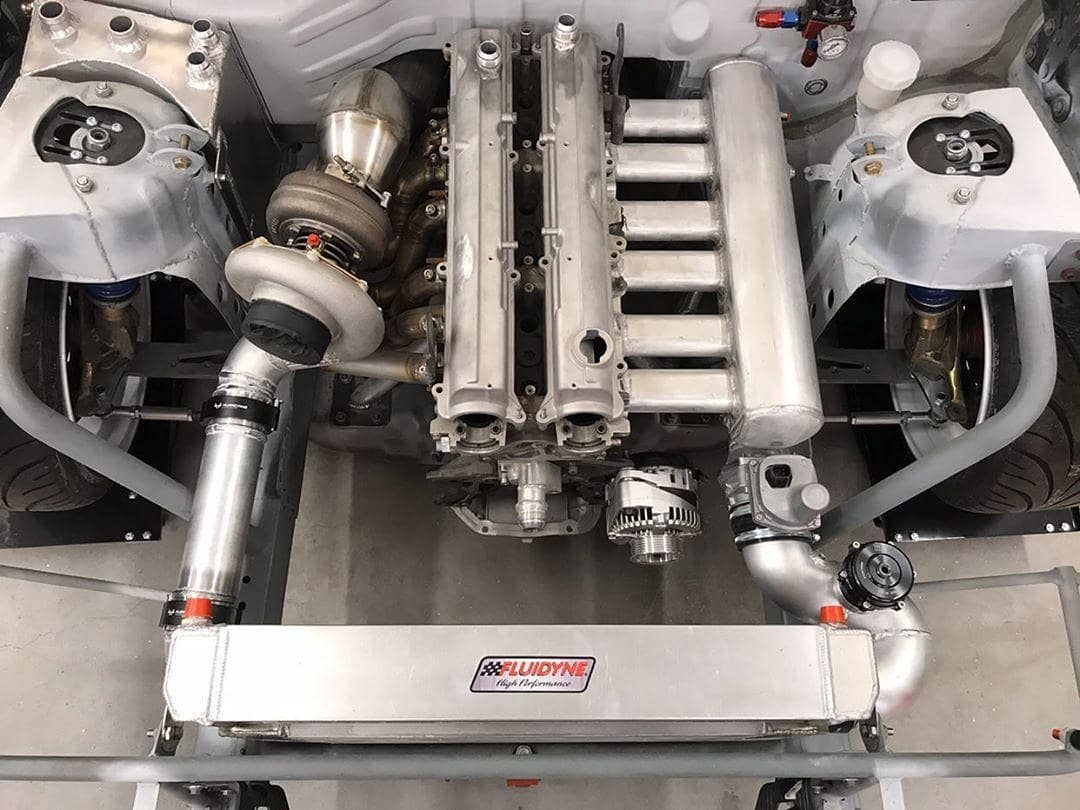
3. Engine
Here you can see a picture where Turbocharger, Intercooler and engine are connected. Without this intercooler, the intake air would have been warmer with lower efficiency as a result.

What does an Intercooler consist of?
An intercooler briefly consists of 3 things:- Intercooler core
- End tanks
- Connections
More information about this:
1. Intercooler core
The intercooler core cools the intake air. It consists of fins where every other layer is rotated 90 degrees. The turbo hot air will cross the ambient air and be cooled down before it reaches the engine.

2. End tanks
The end tanks are welded to the intercooler core and make it possible for pressure pipes to be connected. The end tanks can be shaped as preffered but connections should point out straight for best flow.
![]()
3. Connections
Intercooler connections / end caps can vary in size, but the type of connection can also differ. Sometimes a connection is used for silicone hose and sometimes for Hurricane clamps.

How does an intercooler work?
Hot intake air (Charge air Passages) - From the turbo, hot air is forced in to one side of the intercooler.Cooled intake air (Charged air passages) - The warm intake air from the turbo has crossed with the ambient air through the intercooler core and is now cooler.
Ambient air passages - The ambient air is forced with the wind through the intercooler core and cools hot intake air.
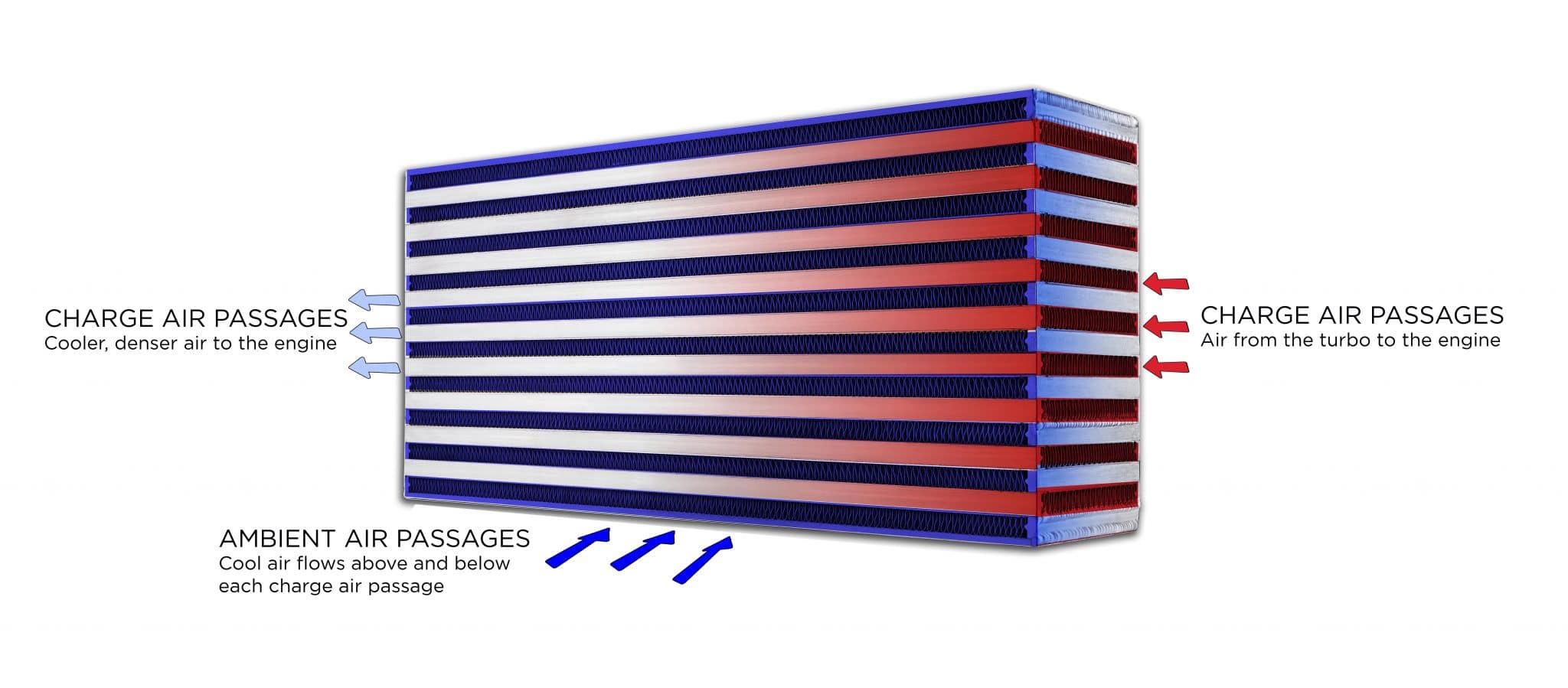
Intercooler installation
Since an intercooler has many joints between all cooling elements / fins and is welded at the ends, it is important to mount this in rubber suspensions. This is to minimize shocks and vibrations.
A leaking intercooler can be difficult to repair, so make a good installation from the beginning to make your intercooler last long.

Intercooler flow - Tip
A tip that applies to all similar types of coolers.
For maximum cooling of intake air, ambient air must be able to pass through the intercooler core unobstructed.
- The ambient air takes the easiest path, so be sure to guide it through the intercooler core by directing the air where you want it. The efficiency of an intercooler can be significantly increased just by passing the air through properly.
- Once passed the intercooler the ambient air must also be able to evacuate in order for new air to pass. If not the case, efficiency will fall again.
- If other coolers are mounted in front or behind, the efficiency is reduced as ambient air flow is restricted.
The conclusion is that ambient air must be routed through the intercooler core and flow freely through and from it.
▼
-
Engine and tuning
- Crankcase ventilation Information
- Engine block: Parts and how they fit together
- Engine deck clearance
- Head gasket - Information
- Engine bearing installation
- Engine bearing Information
- Blow off valve: Information and assembly
- Electronic Throttle Housing - DBW Information
- Noise from engine - Troubleshooting
- ARP bolts: Material and specifications
- Assembly of connecting rods
- Automotive cooling system problem
- Engine cooling system [How does it work?]
- Engine Oil system
- Engine water pump
- Exhaust pipe: Which material should you choose? [+extra information]
- Exhaust system: Parts and assembly
- Exhaust values - Information
- Exhaust wrap
- Intercooler guide
- Oil cooler - Information and FAQ
- Piston ring installation TIPS
- What do notes on Wiseco & JE pistons mean?











































