How does an Ignition Coil work?

Information about ignition coils and how they work. What are the different types, and what should you use? Through the years, many different types of coils and makes have given us invaluable information about what works and what doesn't.
Now, we will go through the parts you need to know to choose your ignition system coils successfully.
- What does an ignition coil do?
- What different ignition systems are there?
- Ignition drive/ignition module
- Terms used
- Connection
- Troubleshooting
1 ▼
What does an ignition coil do?
An ignition coil is briefly explained as being connected between the battery, spark plug, and ECU. The battery charges up the coil like a capacitor. When the control system wants to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the engine's combustion chamber, a signal is sent that releases the energy stored in the coil. This energy is led out through the spark plug where a spark is formed.
2 ▼
What different ignition systems are there?
- Ignition coil (distributor)
With an ignition coil connected to the distributor, the energy generated by the ignition coil passes through an ignition cable to a mechanical ignition distributor. This, in turn, distributes the energy to each ignition cable, which provides voltage to the spark plug/cylinder. This type of ignition coil is used only in older vehicles.
- Coil On Plug (COP)
This coil type is mounted directly to the spark plug, called coil-on plug (COP) or "Pencil coils". They do not require ignition cables as they are mounted directly on the spark plug, where the energy can be generated directly at the plug. The advantage of this assembly is that there is basically no voltage loss caused by ignition cables. In addition, it is a compact solution that gives good space for other things. This also allows for sequential ignition.
- Independent ignition coil (block)
An independent block coil contains several ignition coils that supply the spark plugs with the necessary energy through the respective output via ignition cables. Block ignition coils are offered with single and double spark technology. For performance, the COP variant is used as each cylinder wants separate control (sequential ignition). Double spark technology is called Waste spark and is, as the name suggests, a wasted spark where the coil has had to discharge and charge an extra time per engine revolution.
- Ignition cartridge
This type of ignition type consists of several ignition coils assembled in a "cassette" / a single component. All coils are connected to the spark plugs simultaneously during installation. This type is only used on OEM installations.
3 ▼
Ignition stage/ignition module
An ignition module determines when the voltage from the ignition coil should be transferred to the spark plugs. This module can be integrated into an ignition coil or used as a separate unit.
Separate ignition module/ignition stage
This unit is mounted between the ECU and an Ignition Coil
Dumb ignition coil = 3 pins
This ignition coil does not have a built-in Ignition stage = Ignition module is not built into the coil = A separate ignition module is required.
Smart ignition coil = 4 or 5 pins
This ignition coil has a built-in ignition stage = Ignition module is built into the coil = No separate ignition module is needed
Observera att det kan vara en extra pinne för kabelskärm och/eller extra jord på spolarna. Därför kan antal pinnar vara lite missvisande. För att vara helt säker så bör man se vad tillverkaren säger om just din tändspole.
4 ▼
Terms used
- Waste spark
This is when multiple cylinders share one ignition coil and must discharge/charge 2 times per engine revolution. This places high demands on the ignition system and is not preferable at higher revs, combustion pressure and fatter fuel mixture - Sequential ignition
This is when each cylinder has a separate ignition coil, and the ECU has both the crank and camshaft signal. This way, the coil only discharges/recharges once per engine revolution. This provides a more stable and controllable ignition system, especially at higher revs, combustion pressure and rich fuel mixture. - Dwell
Indicates how many milliseconds (time) an ignition coil needs to fully charge at a certain voltage, e.g. 14V. The coil's "Dwell time" is considered when tuning the ECU, as the time it takes to charge up completely determines how many times it can discharge during a set time.
5 ▼
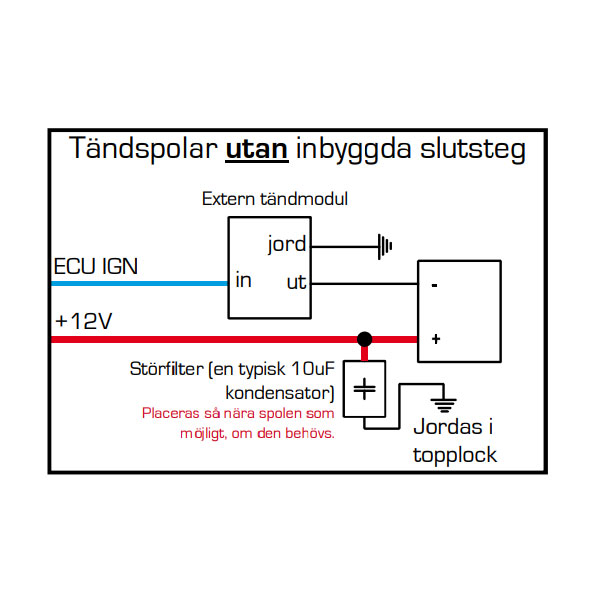
Connection
Connection of ignition coils differs depending on whether the ignition module is built-in or not.
Below, you can see the two different variants.
Dumb coil and Smart coil
Noice filter
Note that you can advantageously fit ignition coil noise filters to minimize electrical interference.

Ignition coil (distributor) connection:
Sw = Switch = Ignition = 15 = + (plus)
Cb = Contact breaker = Trigger / Signal = 1 = - (minus)
6 ▼
Troubleshooting
To check ignition coils/ignition systems, most modern aftermarket ECUs have a diagnostic/test system where you can test inputs/outputs. If you've gone into the control system software and tested the coil outputs (IGN) but still can't get a spark, then one of the following is the problem:
- Cables
The wiring between the ECU and the ignition coil may be broken or damaged, and the signal does not come through. - Connection
The connection of the ignition coil may be incorrect, so the coil does not charge up. Make sure to ground the coil properly! - Coils
The ignition coil or ignition module may be defective / broken - ECU Signal
The least common cause, but if the above parts work, there is a fault in an output from the control system.
▼
▼
-
Engine management / Electric
- Engine control system: The various parts available
- Ignition System Information
- Install motor control
- Pressure sensor - Information
- Temperature sensor - Information
- Buttons - Switches - Information
- Connectors - Information
- Cooling fan car - Information
- Exhaust gas temperature sensor - EGT Sensor
- Lambda sensor - Wide band lambda
- Relay - Information
- Relay box - Fuse central
- CAN protocol - Canbus
- Ethanol sensor - Information
- Gauges and Dash
- Trigger sensor information
- Dimensioning of cable [and fuse size]
- Distributor Problems (And Solution)
- How does an Ignition Coil work?











































